Stem cell research has emerged as one of the most exciting and transformative areas of modern medicine. With the ability to regenerate damaged tissues, repair injuries, and even potentially replace organs, stem cells offer unparalleled potential in the field of regenerative medicine. This article explores the promise of stem cell research, its current applications, and how it is shaping the future of medicine.
What is Stem Cell Research?
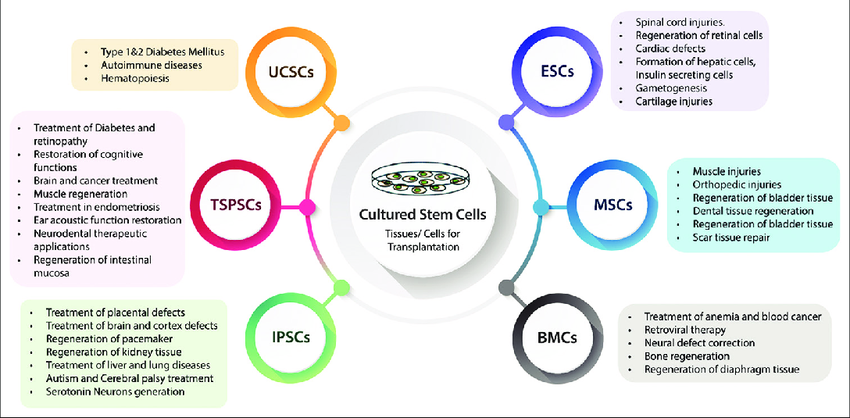
Stem cell research focuses on understanding and harnessing the power of stem cells, which are undifferentiated cells capable of developing into many different types of specialized cells. There are two main types of stem cells:
- Embryonic stem cells: These cells have the potential to develop into any type of cell in the body, making them highly versatile for medical applications.
- Adult stem cells: These cells are more specialized and typically develop into a limited range of cell types, often related to the tissue in which they are found.
Research in this field explores how stem cells can be used to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs, offering hope for a range of medical conditions that were once thought to be untreatable.
How Stem Cells Work in Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine aims to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs through the use of biological therapies, including stem cells. Stem cells have the remarkable ability to differentiate into various types of cells, such as muscle cells, nerve cells, or skin cells, depending on the needs of the patient. This flexibility allows them to be used in a variety of applications, from healing injuries to regenerating entire organs.
1. Regenerating Damaged Tissues
Stem cells can be used to regenerate damaged tissues, such as heart muscle after a heart attack or nerve tissue after spinal cord injury. In cases where the body cannot naturally repair itself, stem cells provide the potential for recovery by generating new, healthy cells to replace the damaged ones.
For example, stem cells are being studied as potential treatments for heart disease, where they could help repair damaged heart tissue and improve heart function.
2. Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering is the creation of new tissues and organs using stem cells combined with scaffolds and growth factors. This technique holds great promise for generating tissues that can be implanted into patients to replace damaged or diseased organs. While still in the experimental phase, tissue engineering has the potential to revolutionize organ transplantation by providing bioengineered tissues that do not rely on donor organs.
3. Cell Replacement Therapy
One of the most exciting applications of stem cells in regenerative medicine is cell replacement therapy, where damaged or dysfunctional cells are replaced with healthy ones derived from stem cells. For instance, stem cells are being used to replace dopamine-producing neurons in patients with Parkinson’s disease, potentially offering a long-term solution to this debilitating condition.
Current Applications of Stem Cell Research in Medicine
Stem cell research is not just a theoretical concept—it is already being applied in a number of real-world medical situations. Some current applications of stem cell therapies include:
1. Bone Marrow Transplants
Bone marrow transplants are one of the earliest and most successful forms of stem cell-based therapies. By transplanting stem cells into a patient’s bone marrow, doctors can treat conditions such as leukemia, lymphoma, and other blood-related disorders. These transplants allow the patient’s body to regenerate healthy blood cells, improving the patient’s immune system and overall health.
2. Treatment of Eye Diseases
Stem cells have shown promise in treating eye diseases, such as macular degeneration and retinal diseases, which can lead to blindness. By using stem cells to regenerate damaged retinal tissue, scientists aim to restore vision and prevent further degeneration. Clinical trials are already underway to evaluate the efficacy of stem cell-based treatments for these conditions.
3. Regeneration of Cartilage and Bone
Stem cells are being studied for their ability to regenerate cartilage and bone, which can be highly beneficial for patients with joint injuries, arthritis, or degenerative diseases. Stem cell-based treatments have the potential to repair cartilage in the knee, hip, and other joints, reducing the need for joint replacements and improving the quality of life for patients.
4. Spinal Cord Injury Treatment
Stem cell research has sparked hope for treating spinal cord injuries, which often result in permanent paralysis. By transplanting stem cells into the injured area of the spinal cord, researchers hope to stimulate nerve regeneration and improve movement and sensation in patients with spinal cord injuries.
The Challenges Facing Stem Cell Research
Despite its vast potential, stem cell research and its application in regenerative medicine face several challenges that must be overcome before it can become a mainstream treatment.
1. Ethical Concerns
The use of embryonic stem cells has raised ethical questions, particularly regarding the destruction of embryos. While adult stem cells do not carry the same ethical concerns, the controversy surrounding embryonic stem cell research has led to strict regulations and limitations in many countries. Researchers must navigate these ethical considerations while advancing the field.
2. Safety and Efficacy
Although early results from stem cell therapies are promising, more research is needed to ensure their safety and effectiveness. In some cases, stem cell treatments have led to complications, such as tumor formation, immune rejection, and uncontrolled cell growth. Ongoing clinical trials and rigorous testing are crucial to understanding the long-term effects and risks of stem cell therapies.
3. Scaling and Cost
Manufacturing and scaling up stem cell therapies is a complex and costly process. Producing large quantities of stem cells for widespread use requires sophisticated techniques and significant financial investment. Additionally, many stem cell treatments are expensive, making access to these therapies limited to only a small group of patients. Efforts are underway to reduce costs and make stem cell-based therapies more accessible.
The Future of Stem Cell Research in Regenerative Medicine
The potential of stem cells in regenerative medicine is immense, and as research continues to advance, we are likely to see even more groundbreaking developments. Some of the key areas where stem cell research is expected to have a major impact in the future include:
1. Personalized Medicine
In the future, stem cell therapies could be tailored to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup. By using a patient’s own stem cells, researchers could create personalized treatments that are less likely to be rejected by the immune system. This could greatly improve the success rates of stem cell therapies and reduce the risk of complications.
2. Organ Regeneration
One of the most exciting possibilities for the future of stem cell research is the ability to regenerate entire organs. While organ transplantation is currently limited by the availability of donor organs, stem cells could provide a solution by allowing researchers to grow functional organs in the laboratory. This would eliminate the need for donor organs and significantly reduce transplant waiting lists.
3. Treatment for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Stem cells hold great promise for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s disease. By regenerating the damaged neurons and restoring lost function, stem cells could offer new hope for patients with these conditions, potentially slowing or even reversing disease progression.
Conclusion
Stem cell research is one of the most exciting and promising fields in regenerative medicine, offering the potential to heal, repair, and regenerate tissues and organs in ways that were once unimaginable. While challenges remain, including ethical concerns, safety, and accessibility, the progress made thus far has been remarkable. Stem cells are already being used to treat a variety of conditions, from blood disorders to eye diseases, and future breakthroughs could lead to cures for debilitating conditions like spinal cord injuries and neurodegenerative diseases.
As research continues and technology advances, stem cell therapies will likely play an increasingly important role in the future of medicine. The potential to revolutionize healthcare through stem cell-based treatments offers hope for millions of patients worldwide, making it a game-changer in the field of regenerative medicine.